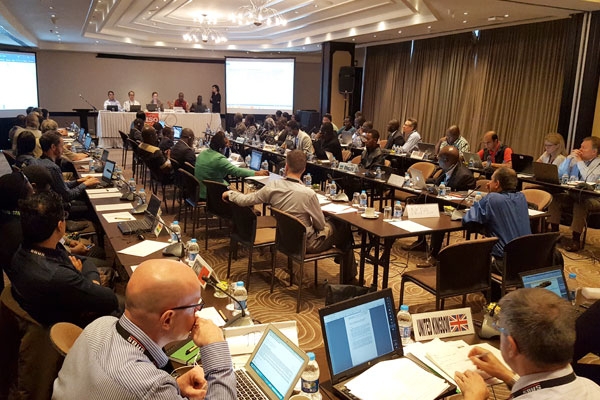
The 94th AfWASA Meetings will be held from November 18-21 in Kampala, Uganda AfWASA to train technicians in municipal project management from July 22-26, 2024 in Douala, Cameroon The African Water Association turns to ‘’African Water and Sanitation Association’’ (AfWASA) The Call for Papers for the 22nd AfWASA International Congress and Exhibition to be held from 16 to 20 February 2025 in Kampala, Uganda is now open

 English
English  Français
Français